
 Cardionerds: A Cardiology Podcast
Cardionerds: A Cardiology Podcast 349. Case Report: Into the Thick of It – An Unusual Cause of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy – Cleveland Clinic
CardioNerds cofounder Dr. Amit Goyal and cardiology fellows from the Cleveland Clinic (Drs. Alejandro Duran Crane, Gary Parizher, and Simrat Kaur) discuss the following case: A 61-year-old man presented with symptoms of heart failure and left ventricular hypertrophy. He was given a diagnosis of obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. He eventually underwent septal myectomy, mitral valve replacement, aortic aneurysm repair, and aortic valve replacement with findings of Fabry’s disease on surgical pathology. The case discussion focuses on the differential diagnosis for LVH and covers Fabry disease as an HCM mimic. Expert commentary was provided by Dr. Angelika Ewrin. The episode audio was edited by student Dr. Diane Masket.
“To study the phenomena of disease without books is to sail an uncharted sea, while to study books without patients is not to go to sea at all.” – Sir William Osler. CardioNerds thank the patients and their loved ones whose stories teach us the Art of Medicine and support our Mission to Democratize Cardiovascular Medicine.
US Cardiology Review is now the official journal of CardioNerds! Submit your manuscript here.

Case Media – An Unusual Cause of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy – Cleveland Clinic
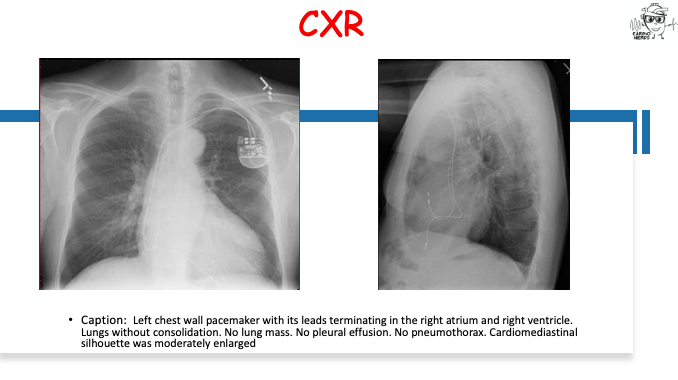

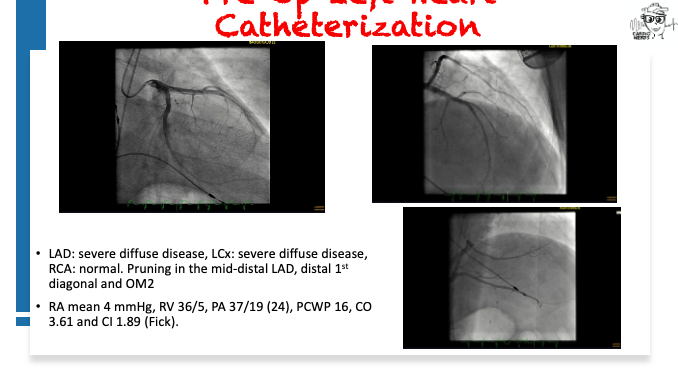
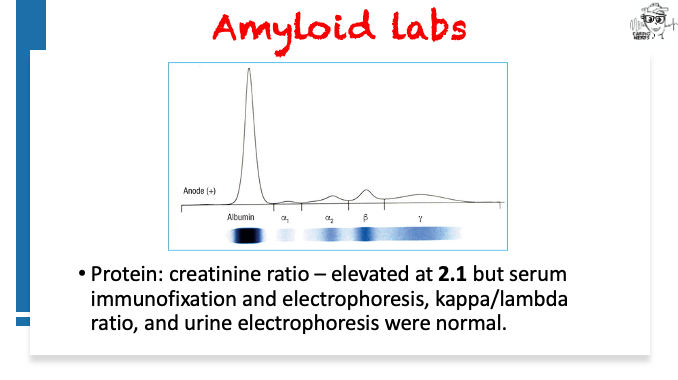
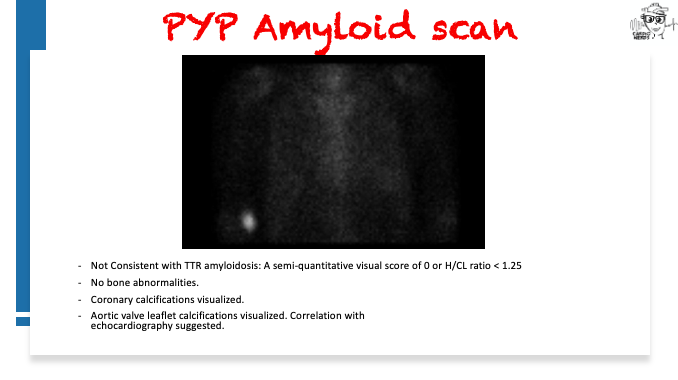
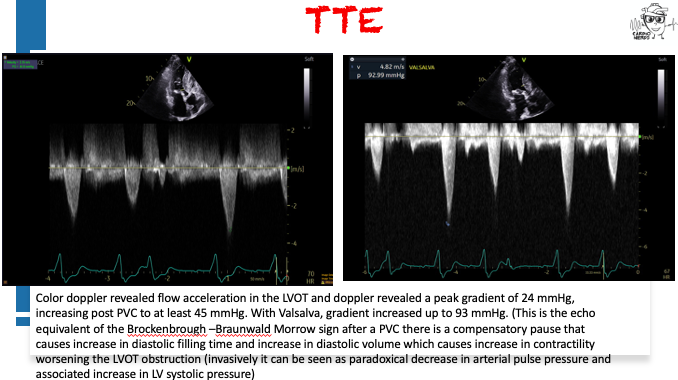
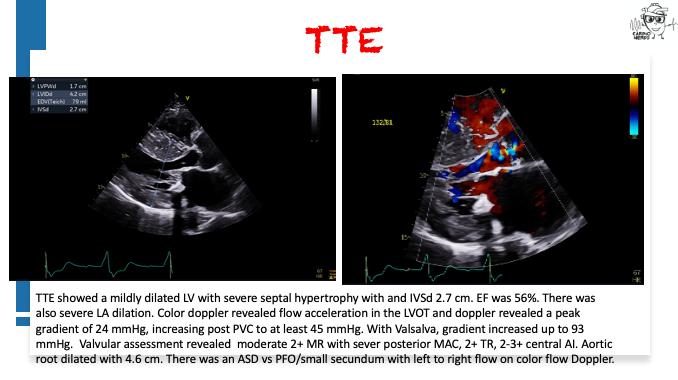
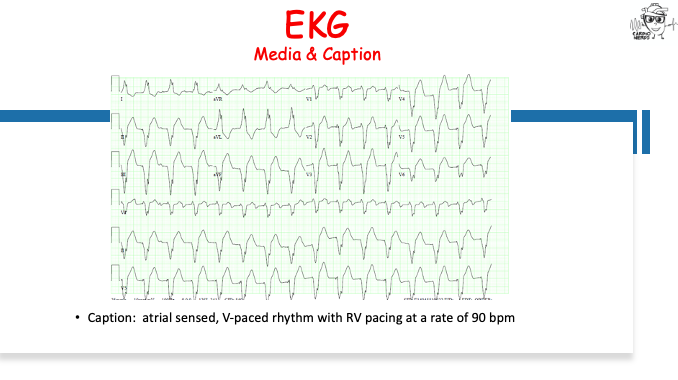
Pearls – An Unusual Cause of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy – Cleveland Clinic
- Left ventricular hypertrophy is a cardiac manifestation of several different systemic and cardiac processes, and its etiology should be clarified to avoid missed diagnosis and treatment opportunities.
- Fabry disease is a rare, X-linked inherited disease that can present cardiac and extra-cardiac manifestations, the former of which include hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, conduction defects, coronary artery disease, conduction abnormalities, arrhythmias, and heart failure.
- The diagnosis of Fabry disease includes measurement of alpha-galactosidase enzyme activity as well as genetic testing to evaluate for pathogenic variants or variants of unknown significance in the GLA gene. Family members of patients diagnosed with Fabry disease should be screened based on the inheritance pattern.
- Multimodality imaging can be helpful in the diagnosis of Fabry disease. Echocardiography can show left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH), reduced global strain, aortic and mitral valve thickening, and aortic root dilation with associated mild to moderate aortic regurgitation. Cardiac MRI can show hypertrophy of papillary muscles, mid-wall late gadolinium enhancement and low-native T1 signal.
- The treatment of Fabry disease involves a multi-disciplinary approach with geneticists, nephrologists, cardiologists, nephrologists, and primary care doctors. Enzyme replacement therapy can delay the progression of cardiac disease.
Show Notes – An Unusual Cause of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy – Cleveland Clinic
What are the causes of left ventricular hypertrophy?
LVH is extremely common. It is present in 15-20% of the general population, and is more common in Black individuals, the elderly, obese or hypertensive individuals, with most cases being secondary to hypertension and aortic valve stenosis. In general terms, it is helpful to divide the causes of LVH into three main groups: high afterload states, obstruction to LV ejection, and intrinsic myocardial problems. Increased afterload states include both primary and secondary hypertension and renal artery stenosis. Mechanical obstruction includes aortic stenosis, subaortic stenosis, and coarctation of the aorta. Lastly, several intrinsic problems of the myocardium can cause LV hypertrophy, such as athletic heart with physiological LVH, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with or without outflow obstruction, and infiltrative or storage diseases such as cardiac amyloidosis, Fabry’s disease, or Danon disease, among others.
How does Fabry disease present?
Fabry disease is present in all races and is an X-linked lysosomal storage disorder caused by pathogenic variants in the GLA gene that result in reduced alpha-galactosidase enzyme activity, leading to accumulation of lysosomal globotriaosylceramide (Gb3) globotriaosylsphingosine (lyso-Gb3) in affected tissues, including the heart, kidneys, vasculature, and peripheral nervous system. The reported incidence of this disease is said to be between 1 in 40,000 and 1 in 117,000 individuals, but screening in newborns suggests that this incidence may be underestimated, as it is present in up to 1 in 8,800 newborns. Depending on the variant of the mutation or the presence of mosaicism in females, the disease can have variable expression with early-onset presentations in the classical form or late-onset presentations in individuals who have residual a-galactosidase enzyme activity.
Fabry disease can have multiple cardiac and extracardiac manifestations. Accumulation of Gb3 occurs in all cell types of the heart, including smooth muscle cells of the endothelium, myocytes, conduction cells, and valvular fibroblasts. Accumulation of glycosphingolipids also leads to biochemical changes in cell function that lead to apoptosis, cellular necrosis, inflammation, and altered membrane ion channel properties that may lead to increased conduction velocities. In the myocardium, cell damage produces LVH and diastolic dysfunction. Damage to endothelial cells leads to coronary artery disease and myocardial ischemia. Together, these changes may eventually lead to myocardial fibrosis and systolic dysfunction. Involvement of the conduction cells can manifest as conduction abnormalities and ventricular arrhythmias. Other electrocardiographic findings are a short PQ interval or chronotropic incompetence. Aortic remodeling in FD has been well described and often presents as sinus of Valsalva dilatation or ascending aortic aneurysm, which in turn may lead to secondary aortic regurgitation.
Extracardiac manifestations of Fabry disease include neuropathy, gastrointestinal symptoms, angiokeratomas, cornea verticillata (golden-brown or gray discoloration of the corneal epithelium), hypohidrosis and exercise intolerance, proteinuria and renal failure, juvenile or cryptogenic stroke, hearing loss, chronic white matter hyperintensities in brain MRI, and lymphedema.
How is Fabry disease diagnosed?
Diagnosis of Fabry disease should be suspected in patients with unexplained LVH, especially when there are any extracardiac red flags. LVH presents in more than half of men and more than a third of women after the third decade of life. Other electrocardiographic findings besides high QRS voltages may include inferolateral negative T-waves, short PQ intervals, and a reduced P wave duration. The diagnosis is confirmed through genetic testing that may identify pathogenic variants as well as variants of unknown significance. Enzymatic level activities should be measured as well for confirmation. Absent or reduced alpha-galactosidase activity levels coupled with pathogenic variants in genetic testing confirm a diagnosis of FD. Variants of uncertain significance might require confirmation by endomyocardial biopsy and by lyso-Gb3 level assessment.
What is the role of cardiovascular imaging in the diagnosis of Fabry disease?
Multimodality imaging may be helpful in the diagnosis and staging of FD. Echocardiography typically reveals LVH with disproportionate hypertrophy of the papillary muscles, loss of base-to-apex circumferential strain gradient, and right-ventricular hypertrophy with normal systolic function. There may also be abnormal thickening of the aortic and mitral valves. Global longitudinal strain and speckle tracking may allow for early detection of cardiac involvement in patients with pathogenic variants.
Cardiac MRI (CMR) may help with tissue characterization. Typical CMR findings of FD include late gadolinium enhancement (LGE), initially in the basal inferolateral wall, and low native T1 signal intensity, likely reflecting glycosphingolipid myocardial storage and occurring before the development of significant LVH. Tissue characterization by CMR also allows for staging of FD cardiomyopathy in different and progressive stages of accumulation, with progressive lowering of T1 signal intensity; inflammation and hypertrophy, with low T1, initial LVH, and T2 mapping showing inflammation in the basal inferolateral segment associated with LGE; and fibrosis, with increasing T1 values or pseudo-normalization and LGE with wall thinning in the basal inferolateral segment.
What is the management for Fabry disease?
The main objective in the treatment of FD is prevention of disease progression and end-organ damage. The mainstay of therapy is enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) with agalsidase-alfa or beta intravenous injections every other week. Agalsidase-alfa is produced in human cell lines, while the beta form of the enzyme is produced by recombinant DNA technology using mammalian cells.
ERT is indicated in patients with late-onset FD who have the presence of laboratory, histological, or imaging evidence of injury to the heart, kidney, or central nervous system. It can delay the progression of cardiac disease and reduce the cardiovascular event rate in patients with FD.
Another available pharmacological agent is the chaperone agent migalastat, which can be helpful for specific genetic variants of FD by stabilizing the translated form of alpha-galactosidase. This chaperone agent is given in oral tablets every other day. There is ongoing development of novel therapies for FD with second-generation ERTs, substrate reduction therapies, and gene and mRNA therapies.
References – An Unusual Cause of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy – Cleveland Clinic
- Weidemann F, Strotmann JM, Niemann M, et al. Heart Valve Involvement in Fabry Cardiomyopathy. Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology. 2009;35(5):730-735. doi:10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2008.10.010
- Pieroni M, Moon JC, Arbustini E, et al. Cardiac Involvement in Fabry Disease: JACC Review Topic of the Week. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2021;77(7):922-936. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2020.12.024
- Barbey F, Qanadli SD, Juli C, et al. Aortic remodelling in Fabry disease. European heart journal. 2010;31(3):347-353. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehp426
- Chimenti C, Morgante E, Tanzilli G, et al. Angina in fabry disease reflects coronary small vessel disease. Circulation Heart failure. 2008;1(3):161-169. doi:10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.108.769729
- Linhart A, Germain DP, Olivotto I, et al. An expert consensus document on the management of cardiovascular manifestations of Fabry disease. European Journal of Heart Failure. 2020;22(7):1076-1096. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/ejhf.1960
- Tower-Rader A, Jaber WA. Multimodality Imaging Assessment of Fabry Disease. Circulation Cardiovascular imaging. 2019;12(11):e009013. doi:10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.119.009013
- Germain DP, Charrow J, Desnick RJ, et al. Ten-year outcome of enzyme replacement therapy with agalsidase beta in patients with Fabry disease. Journal of Medical Genetics. 2015;52(5):353 LP – 358. doi:10.1136/jmedgenet-2014-102797
- Pieroni M, Moon JC, Arbustini E, et al. Cardiac Involvement in Fabry Disease: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021;77(7):922-936. doi:10.1016/J.JACC.2020.12.024
- Maron BJ, Desai MY, Nishimura RA, et al. Diagnosis and Evaluation of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022;79(4):372-389. doi:10.1016/J.JACC.2021.12.002
- Bornstein AB, Rao SS, Marwaha K. Left Ventricular Hypertrophy. StatPearls [Internet] Treasure Island (FL). Published online August 8, 2022. Accessed April 1, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557534/
